Anatomy of Healthcare App Development
Table of Contents
Healthcare applications bridge the gap existing in medical aid delivery. The applications facilitate affordable and convenient healthcare services for everyone, especially those in underserved areas.
Driven by effective planning and administration, healthcare applications can provide virtual consultations, improve patient access to medical specialists, and get personalized care.
To launch a market-ready healthcare application, you need to be clear about the features to add, compliances, security, and designing, among other aspects. Dive into our comprehensive guide on healthcare app development, covering everything from crucial features to future trends;
- Importance of healthcare applications
- Types of healthcare applications
- Key Features of Healthcare Applications
- Healthcare app development process
- Healthcare-related regulations to follow
- Challenges for healthcare app development
- Future trends in healthcare application development
Towards the end, we will also share a couple of case studies demonstrating our expertise and experience in building healthcare applications.
Growing Importance of Healthcare Applications
The usage of telehealth solutions has increased by 38X from the pre-COVID-19 baseline. The rampant digitization of the medical industry makes healthcare more accessible and affordable, fueling rapid growth. Hence, more industry players are investing in consumer-friendly healthcare applications in different domains.
Well-planned healthcare applications provide improved access to healthcare while empowering a self-management system with trackable health metrics through wearables connected with applications.
These apps help build personalized care schedules and offer recommendations based on the current situation and real-time data insights. Real-time data unlocks valuable insights into patient preferences, allowing companies to tailor their apps for maximum adoption and enhance healthcare accessibility. They also improve communication and data sharing to improve care coordination and let users schedule appointments and access medical records through a single platform.
On the other hand, businesses are exploring new ways to build and distribute advanced healthcare solutions, especially knowing that the global mHealth app market will grow to $861.40 billion by 2030.
So, where businesses want a share of this market’s potency, they also wish to improve patient satisfaction and increase loyalty, mostly by building a healthcare application with a specific purpose.
Types of Healthcare Applications
Before diving into healthcare app development, choose the right type of app for your vision. Go for a focused solution, not a one-size-fits-all attempt. It’s not ideal to build one application that can do everything, at least not initially. Here are the types of healthcare applications to check out for development.
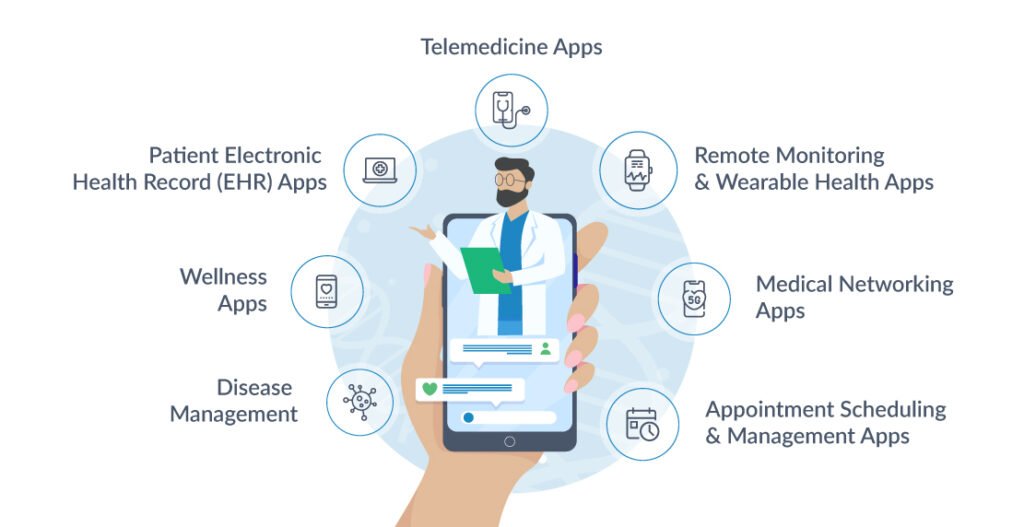
Telemedicine Apps
Telemedicine applications bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers. Patients can use these applications to receive medical advice, treatment, and diagnosis reports from doctors without physically visiting the doctor.
Secure video, audio, or text channels enable convenient consultations within the app. The benefits you can provide to the users with a telemedicine application include;
- Eliminating wait times for doctor consultations
- Reducing costs by eliminating travel
- Ensuring healthcare services reach underserved populations
Tailor features based on your chosen specialty, like pediatrics, dermatology, or mental health.
Examples; Amwell, Teladoc Health, MDLIVE, and HealthTap.
Remote Monitoring and Wearable Health Apps
Wearables include fitness trackers and smartwatches with health parameters tracking functions. Develop companion apps for wearables, letting users track and share health data effortlessly.
These applications track and store health-related data and inform users when the selected parameters cross the allocated range. The application you build can be retrofitted to send alarms and notifications to healthcare providers and families when certain health parameters reach an alarming level, facilitating quick and timely response.
Examples: Jotform, Dexcom, Senseonics, and Medtronic.
Medical Networking Apps
These applications cater to social networking among healthcare professionals. Even though all medical professionals can interact and communicate over other generally available platforms, a specific platform built for them can serve them better.
Medical networking applications are built to help healthcare professionals connect and interact with their peers and colleagues. Curofy facilitates case discussions and knowledge sharing among doctors and helps find cures faster. Moreover, Docplexus is another similar application built for knowledge sharing.
Appointment Scheduling and Management Apps
Appointment scheduling applications help patients find the doctor they need and set an appointment at a mutually comfortable time. Doctors can upload their schedules on the application, and patients can book a slot after checking these schedules.
Doctors and their assistants can use these apps to manage appointments, receive payments, and share patient information.
Examples; Doctor’s Note App, Practo, Lybrate, Doctor on Demand, etc.
Patient Electronic Health Record (EHR) Apps
EHR applications and solutions help medical professionals track, store, upload, and collect medical information about a patient on a single shared or exclusive platform.
Building a solution around extracting and uploading data on EHR applications saves time and eliminates manual errors. Medical professionals can exchange patient data through the same application, leading to quick and easy access.
Examples; DrChrono, Practice EHR, AdvancedMD Mobile, and NextGen.
Wellness Apps
Healthcare wellness applications provide health-related services and suggestions concerning the patient’s requirements. With wellness applications, a better approach would be to focus on one niche initially. You can choose from different niches like emotional wellness, sleep tracking, therapy, etc. After finding success in any one of the domains, you can continue to add more and enhance the scope of services.
You can either start an application offering services in one of the subjects or include it all in a single application.
Examples; Headspace, Mepreg etc.
Disease Management
Disease management applications help manage chronic diseases requiring regular monitoring and effective management. Some key features of these applications include health parameter tracking, medicine reminders, remote monitoring, and self-management.
Examples; MyTherapy and My Pain Diary.
Your decision to build any of the above types of healthcare applications must be motivated by the potential to build a better product than what is available in the market.
Key Features of a Successful Healthcare Application
While features may vary based on the app’s purpose, these key elements consistently contribute to a successful healthcare application. However, the following are the key features almost always present in a healthcare application.
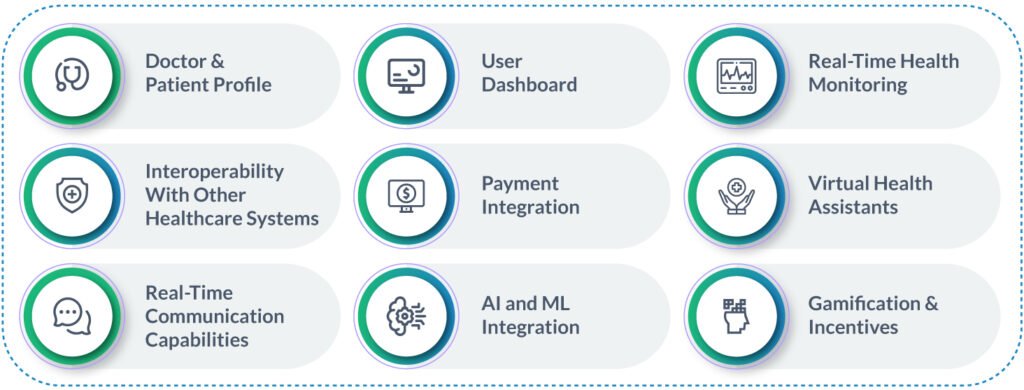
Doctor And Patient Profile
Doctor and patient profiles in a healthcare application for convenient health and personal data access. Profile creation and management for patients means they can organize their medical health records, test results, prescribed medications, etc.
Doctors can leverage the profile feature to share their specialty and qualifications.
Where doctors can also view patient profiles to access relevant information, the patients can also check doctor profiles to know more about their doctor. Patients can use this information to decide whether to consult the doctor.
Interoperability With Other Healthcare Systems
Healthcare applications with this feature facilitate continuity of care for the patients as all authorized medical professionals can access the patients’ medical records and history.
Interoperability improves care, accuracy, and efficiency by readily accessing medical records. With the rapid increase in harnessing wearables for healthcare, interoperability is even more crucial to integrate all relevant data and make it accessible.
Real-Time Communication Capabilities
Setting communication standards between doctors-doctors and doctor-patient through the application is critical in healthcare services delivery. Instant communication is essential for telemedicine, telehealth, and appointment schedule healthcare applications.
Real-time communication fosters faster consultations, diagnoses, and improved access to healthcare, especially in underserved areas. Moreover, communication can play a critical role in managing chronic conditions while ensuring personalized support and reassurance to the patients.
User Dashboard
User dashboards are relevant to both doctors and patients. The dashboard gives their respective users a complete overview of the relevant information with real-time updates.
Doctors can use them in multiple ways, including patient overview, appointment scheduling, and management-related applications. The doctors can check the dashboards for necessary information on the patient to make clinical decisions. They can also use these dashboards to manage their daily appointments and check timings, meetings, schedules, etc.
These dashboards, when added to a patient-centric application like medicine management, disease management, telehealth, wellness, etc. can become a single source of information. A glance at the dashboard gives enough information to the patients about their medicine, health parameters, doctor appointments, etc.
In both cases, the dashboards are linked with their respective exclusive pages if the users require additional information.
Payment Integration
Add multiple secure payment gateways to the application, ensuring that your users don’t lose customers for the lack of payment options. You can use APIs to add debit and credit cards, Stripe, PayPal, Apple Pay, GPay, and other modes of payment.
A payment gateway is essential for all healthcare apps offering premium services, subscriptions, and consultation appointments.
AI and ML Integration
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have multiple use cases in different healthcare applications. AI and ML algorithms are used for tasks like early diagnosis of health conditions and diseases like cancer, heart issues, Alzheimer’s etc.
AI and ML enabled data analysis to automate analytical model building, identify patterns, and extract patient-related information from data. It can also assist in data de-identification, which is required to remove or hide personally identifiable information from datasets, including names, addresses, etc.
Integrated within healthcare apps, AI can analyze medical images faster and more accurately. Moreover, AI-powered chatbots can manage the basic tasks for doctors, like booking appointments, answering limited user queries, etc.
Patient-oriented AI assistants can promote medication adherence, track vitals, and offer personalized feedback for better health management. Together, wearables and AI-ML applications can track a patient’s symptoms and monitor vital signs to send alerts on time.
Real-Time Health Monitoring
Real-time health monitoring creates room for proactive intervention through early detection of potential health issues. For instance, heart rate monitoring wearable devices linked with applications can send alerts for abnormal heartbeats.
Similarly, observing the real-time data on medication, patient activity levels, and vital health parameters helps optimize treatment plans. Most importantly, real-time health monitoring helps address issues before they turn critical.
Other benefits of this feature include better awareness, motivation, and reduced anxiety due to timely and effective management.
Virtual Health Assistants
Virtual health assistants (VHAs) can provide patients with 24/7 support and personalized guidance. By offering reassuring answers and guidance, the VHAs can also reduce a patient’s anxiety and provide medically relevant information tailored to the individual’s needs.
These VHAs can automate routine tasks for medical professionals like appointment scheduling, prescription refills, collecting data, and making notes.
Gamification And Incentives
Adding Gamification elements like points, progress bars, challenges, badges, and leaderboards will motivate the users to stick to schedules, maintain health, complete exercises, etc.
For instance, a self-management application for heart disease has gamified elements to motivate users to walk more and move or hydrate through interactive elements. They ask users to complete challenges and earn reward points, etc.
These gamified elements offer personalized rewards and challenges according to the user’s needs and preferences. Gamification provides positive reinforcement and instills a sense of accomplishment, fostering continued engagement and adopting a health-conscious lifestyle.
Implementing these features based on your app’s needs enhances its uniqueness and drives user adoption.
In addition to these trending features, also add basic features like signup, user onboarding, login, push notifications, reminders, etc.
Healthcare App Development Process | What Steps to Follow
From idea conceptualization to product launch, following a specific and well-oiled development process is essential. While specific features may vary, the core development process follows a similar roadmap for most healthcare applications.
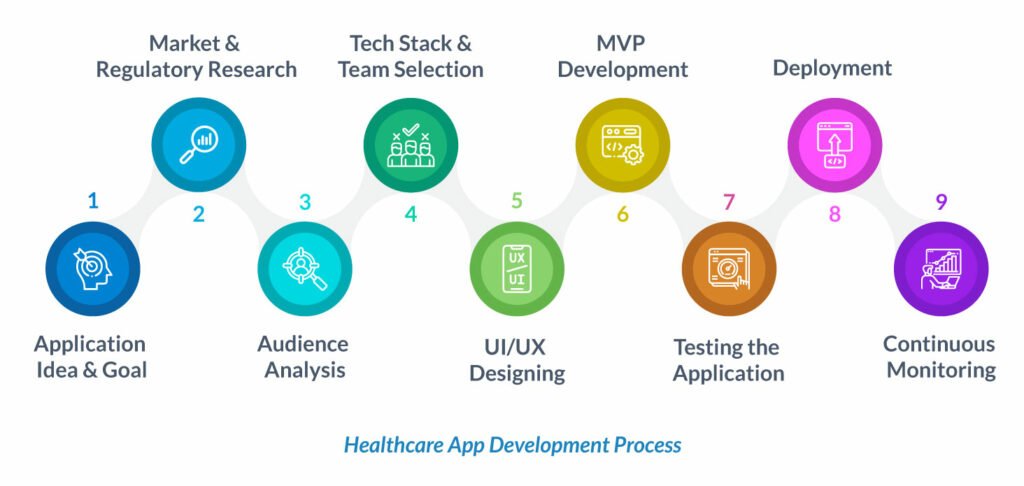
Application Idea And Goal
Begin with researching your users and their pain points and understanding their needs. You must find a way to address their problems and fill the gap, building your application to them.
Start with general research and then niche down into a specific issue you will address with your solution.
Market and Regulatory Research
Healthcare applications are subject to strict regulations in almost every part of the world. While some regulations are country-specific, others are globally relevant. Ensure that you consult legal and regulatory experts to understand your application’s applicable compliances.
Market research starts by surveying the existing healthcare app landscape. Find the leading competitors in your niche, their strengths and weaknesses, and potential market gaps. Identify these market gaps as opportunities to introduce your unique solution and capture audience interest.
Audience Analysis
Decide who you are targeting. Is your application for patients, healthcare providers, or both? For each type of user, create detailed user personas, defining their demographics, pain points, and technical expertise.
Take into account the patient’s perceptual, motor, and cognitive capabilities. Elderly people are less tech-savvy than younger generations. Hence, the choice of features, how the interface flows, and accessibility must be catered to make their user experience smooth.
Tech Stack and Team Selection
When choosing the tech stack for a healthcare application, consider the applicable frameworks from a long list, which includes names like Flutter, Xamarin, MS .NET Platform, and Opal (Built on Django).
While choosing the tech stack, go for technologies that can help achieve capabilities like interoperability, scalability, and integration with other healthcare systems.
You may find some percentage of users are using legacy systems in their hospitals. Hence, try to include systems in your application, ensuring interoperability with these systems.
Consider a team with healthcare app development experience and expertise for team selection. Also include medical advisors and regulation and compliance experts to the team.
UI/UX Designing
Designing a user-friendly and interactive user interface in healthcare applications is crucial. An app’s UX can impact the medical outcomes and the well-being of the patients. Additionally, while designing the app, ensure accessibility and a positive user experience.
Research from the Journal of American Medical Informatics Association highlights key aspects of developing an elderly-friendly healthcare app;
- Cater to users with vision impairment.
- Consider motor coordination problems.
- Ensure consistency in layout to manage memory deterioration.
- Add audio alternatives for text.
Prioritize user-centric design principles by ensuring intuitiveness, smooth navigation, and clear information presentation. Avoid overwhelming your users with too many colors, complex information, and components on a single screen.
MVP Development
Instead of building a feature-packed solution, focus on building a minimum viable product with the core functionalities to solve the identified problem effectively. However, even in the MVP approach, you cannot ignore the compliances, accessibility, and security aspects.
Testing the Application
Perform comprehensive tests on the application to assess and improve functionality, usability, security, and performance. Also, focus on user testing with the parameters specific to your target audience.
Administer compliance testing specific to the target country and the applicable regulations. After standard testing is complete, conduct pilot tests in real-world settings.
Launch the application as a beta version for specific healthcare institutions or patient groups. Utilize beta testing feedback and real-world data to refine the app before public release.
Deployment
Focus on App Store Optimization (ASO) as you launch the application on app stores for the target audience. Always optimize the application listing with relevant keywords and catchy descriptions to improve app discoverability.
With the application launch, focus on marketing and user acquisition through different channels. Explore organic marketing along with utilizing social media and targeted advertising to acquire customers.
Continuous Monitoring
The healthcare app development doesn’t end with deployment. After the launch, your focus should be on consistently extracting data insights and analytics to monitor user behavior and identify areas of improvement. Build an app improvement cycle to integrate changing user preferences and market trends.
Navigating the Regulatory Framework for Healthcare Apps
Healthcare apps handle sensitive data concerning individuals and healthcare organizations. Considering the impact of what can happen if this data becomes public knowledge, governments across the globe have set some regulations.
Every application eligible to be a healthcare application must fulfill the following compliances. This list provides a general overview and isn’t exhaustive. Consult a compliance expert or a team like DigiCorp for specific regulations relevant to your country and app type.
- HIPAA: Applicable in the USA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act protects an individual’s privacy and secures identifiable health information. It instructs organizations to take measures for safeguarding patient data, ensuring confidentiality, and building trust.
- FDCA: The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act is applicable in the USA and regulates the safety plus effectiveness of medical devices, including mobile applications. Under FDCA, the application’s quality and security must protect users and institutions from potential harm.
- DQSA: Drug Quality Services Act applies to healthcare applications as it instructs to ensure data quality and accuracy while recommending smooth information exchange. As a result, the patient records are always secure and accurate, and the healthcare organizations can build an efficient system.
- HiTech: The HiTech Act, an extension of HIPAA applies to healthcare providers and healthcare clearing houses along with their business associates. These entities must follow the regulations under the HIPAA and HiTech Act if they are involved in creating, receiving, maintaining, and transmitting Protected Health Information (PHI). Applications tracking user’s health, fitness, and wellness data may not fall under the HiTech Act’s scope. However, if these applications exchange data with the EHRs or are facilitated by healthcare providers, they may fall under the HiTech Act and HIPAA.
- NIST: National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework sets the guidelines for mitigating cybersecurity threats. NIST sets best practices for building secure healthcare infrastructure and protecting patient data and institutions.
- Health Level 7: HL7 sets the groundwork that businesses must follow to ensure standards are met for exchanging medical information between healthcare providers. Apps exchanging medical information must adhere to HL7 standards for data interoperability.
While following these compliances, organizations building healthcare applications should look into data encryption and data identification. The regulations and compliances are also subject to change, and their application can vary according to the region. Stay updated with the compliances and seek legal advice to fulfill specific requirements.
Challenges in Healthcare App Development
When following the right approach, building the best possible healthcare application for your target audience becomes easier. However, there are some challenges you may encounter along the way.
Here are the most common challenges businesses face in healthcare app development and tips on overcoming them.
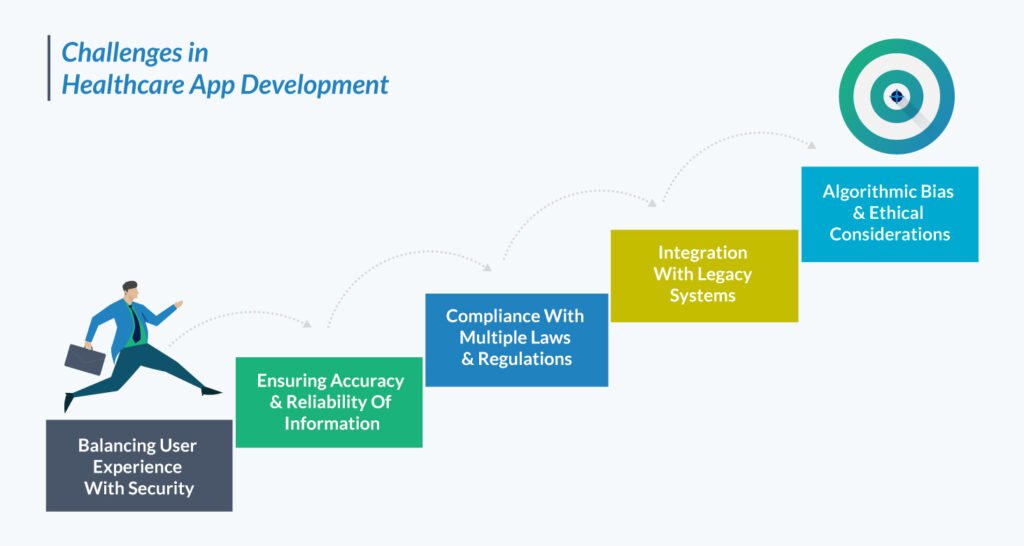
Balancing User Experience With Security
Healthcare apps need robust security measures like multi-factor authentication, data encryption, etc., which increases friction to the user experience. Plus, the need to ensure user privacy and transparency limits personalization.
To balance UX and security, build intuitive designs and clearly explain the data security measures implemented to reduce friction. Simplify access to information and allow users to opt into enhanced features with stricter security protocols.
Ensuring Accuracy And Reliability Of Information
Partner with reputable medical institutions to curate accurate and reliable information. Employ fact-checking tools and regularly update content to combat misinformation.
To overcome this, establish a solid healthcare-related database shared by reputable institutions. Regularly check for content and regulation updates manually or employ AI-powered fact-checking tools.
Compliance With Multiple Laws And Regulations
You will find a dedicated section on healthcare-related compliances above. Following these compliances is a big challenge, especially if you are not taking professional assistance.
Frameworks and laws heavily regulate healthcare products. The complex web of regulations demands expert guidance. Consider collaborating with compliance specialists to ensure thorough adherence.
Integration With Legacy Systems
Integrating modern-day software and applications with legacy systems is challenging due to technical incompatibility, lack of documentation, and standardization. Moreover, security concerns within the legacy systems increase security vulnerabilities.
Instead of building end-to-end systems for integration, build open APIs for legacy systems that can bridge the gap between old and new systems. Prioritize secure data migration and meticulous information exchange to minimize vulnerabilities. A phased healthcare app development and integration approach can minimize disruption.
Algorithmic Bias And Ethical Considerations
Be careful when integrating AI and ML algorithms into the application, as biased data leads to inaccurate diagnosis and wrong treatment. Plus, some black box algorithms don’t share how they reached the conclusion, and using them hinders trust and accountability in the application you will build.
Combat bias by utilizing AI and ML models trained on diverse, unbiased datasets. Leverage human excellence in leveraging AI models to understand any potential biases.
Future Trends in Healthcare App Development
As you are planning to build a healthcare application in 2024, familiarize yourself with the upcoming trends relevant to this industry.
- Virtual Reality And Augmented Reality: AR and VR technologies are going to facilitate phobia treatments in virtual environments. Surgeons will use the VR systems to practice complex surgeries with simulations. The AR technology can guide medication adherence with interactive step-by-step overlays for older patients.
- Big Data: Big data analytics can decipher vast datasets to predict disease risks and tailor treatment plans. For instance, it can help design cancer treatment specifically for the patient’s unique tumor profile. It can also identify subtle patterns in health data, enabling early detection of diseases and mental health issues.
- Patient-Generated Health Data: Patients will supplement the existing medical information with digital solutions either by sharing them with the concerned entities or submitting the missing data. This is going to build a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health, facilitating accurate diagnosis.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: RPM applications and devices regularly scan patient health and integrate the data into a comprehensive database. RPM is instrumental for patients who cannot visit the hospital regularly but need regular attention. The healthcare providers with access to the RPM database can review the submitted data and provide the required assistance.
- AI-Based Symptom Checking: The upcoming AI systems can provide information about a condition with text, video, or image as context. Imagine clicking a picture of a rash or making a video of the patient, allowing the AI system to provide potential causes, diagnoses, and recommended actions.
Hire Digicorp as your Healthcare App Development Partner
In today’s rapidly changing healthcare landscape, it is essential to partner with a development team that is both flexible and dynamic, with the necessary industry expertise and vision to help you stay ahead of the curve.
With Digicorp as your healthcare app development partner, you benefit from two decades of healthtech industry experience. We have an impressive portfolio that includes innovative solutions like EHRs for Clinic, EHRs for Nursing Homes, EHRs for Hospitals, and other Health and Wellness Apps.
To get more insights into our expertise in developing mass adoption-ready applications in the healthcare domain, here’s a quick way to get started.
Sanket Patel
- Posted on February 14, 2024
Table of Contents


